
Photo by Point3D Commercial Imaging Ltd. on Unsplash
We can take some simple steps to conserve water by altering our daily habits, which helps reduce wasteful usage of this critical resource. U.S. property owners are also encouraged to transition to higher-efficiency appliances, fixtures and components. Now more than ever, high-efficiency toilets, faucets and other household products are available, and they use less water than traditional alternatives.
Humans rely on clean water for many reasons and often take easy access to it for granted. While water scarcity has traditionally been a problem in underdeveloped countries, it is also increasingly a concern in many areas of North America. The decreasing water supply in the U.S. and Canada should be no surprise, considering the large quantities we consume relative to other countries.
The following table contains data from The Water Project, Inc., a non-profit organization, which reveals the average gallons of water used per person each year.
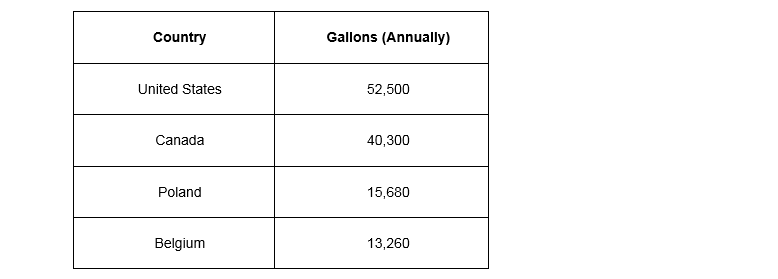
Aside from excessive water use, North America’s decreasing freshwater supply is also exacerbated by drought, rising temperatures, agricultural industry demand, pollution and losses from leaks across our deteriorating infrastructure. U.S. states, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico and Utah, are among those with the most significant scarcity problems.
In the U.S., a large percentage of the water used each day occurs in bathrooms. For example, approximately 40% of overall water use in the average U.S. household results from flushing toilets, and more than 30% stems from using bathtubs and showers.
How Can Homeowners Conserve Water by Changing Habits in Bathrooms?
We can substantially reduce water waste by making some minor changes to our daily bathroom routine. Among the most effective practices involves simply shutting off running water. For example, turn off the water while brushing your teeth and while you rub soap and water on your hands until you are prepared to rinse.
When shaving, less water is typically used by filling the sink with water once instead of continually running the faucet. Keep in mind that maintaining a supply of hot water uses more energy compared to cold water; therefore, use cold water when possible.
Generally, taking a shower uses less water than taking a bath. When taking baths, reduce the water level by a few inches.
High-Efficiency Toilets
The bathroom toilet is a comparatively large consumer of water. Outdated, inefficient models often use more than five gallons of water in a single flush. Today, many toilets use less than 1.3 gallons of water per flush while still performing well.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is a leader in conserving water and reducing water waste. The EPA’s WaterSense program is an impactful, ongoing effort to save water. A key aspect of the WaterSense program involves assessing and labeling products that meet its standards for efficiency. In general, products that demonstrate efficiency equating to at least 20% savings are designated as WaterSense certified.
When it comes to toilets, the WaterSense program has recognized the importance of ensuring that high-efficiency toilets also meet reasonably acceptable performance standards. During the 1990s, toilet manufacturers aggressively pursued WaterSense certification and governmental compliance standards by creating innovations such as “low-flow” toilets.
For example, the Energy Policy Act of 1992 established a new standard for toilets, which created a threshold of using a maximum of 1.6 gallons of water per flush. In response, many manufacturers simply created toilets with smaller tanks and reduced the amount of water expended per flush. Unfortunately, consumers quickly expressed dissatisfaction with many of these earlier high-efficiency models, as they often required multiple flushes to completely remove all toilet bowl contents.
In recent years, toilet manufacturers have developed better ways to balance efficiency and performance. Currently, the criteria for water efficiency of single-flush toilets are a maximum of 1.28 gallons of water per flush.
Showerheads
The average family in the U.S. uses almost 40 gallons of water per day bathing. According to The World Population Review’s 2024 report on bathing habits, approximately 90% of Americans take showers rather than baths.
As with toilets, the Energy Policy Act of 1992 also established standards designed to conserve water in showerheads, which are defined as accessories used to sprinkle or spray water onto bathers, generally from an aerial (overhanging) position. The threshold created at this time was 2.5 gallons of water per minute.
Today, shower heads that meet WaterSense standards use a maximum of 2 gallons of water per minute while still satisfying the performance expectations for water spray intensity and coverage. An average U.S. family could save roughly 2,700 gallons of water in one year by installing WaterSense-approved options.
In terms of performance, WaterSense requires that showerheads deliver water at a minimum flow rate of 20 psi, which generally provides sufficient spray force and spray coverage to achieve “user satisfaction.”
Keep in mind that showerheads primarily deliver hot water, which uses additional energy as needed for the home’s water heater. Using a WaterSense-labeled showerhead might save a household more than 300-kilowatt hours of electricity in one year.
Faucets
Bathroom or lavatory sink faucets are also heavily used accessories in daily life. The general, standard bathroom sink faucet delivers a water flow of approximately 2.2 gallons per minute, and most models include an aerator.
Today, faucets that earn the WaterSense label use no more than 1.5 gallons of water per minute, which equates to roughly a 30% savings over the industry standard. According to user satisfaction reports, WaterSense determined that no “noticeable” differences were experienced at the 1.5 gpm flow rate. American families who transition to a WaterSense-approved faucet may save up to 700 gallons of water annually.
Many thousands of WaterSense labeled models exist in the market today, which also helps to ensure that property owners will find a faucet that appeals to them aesthetically. Several U.S. states, including California, Hawaii and Washington, now have residential lavatory restrictions of 1.2 gpm.
The Importance of Promptly Detecting and Repairing Bathroom Water Leaks
The most common bathroom water leaks are dripping faucets and showerheads, leaky valves, and running toilets. A leaky faucet might generate one drip per second, which could translate to losing over 3,000 gallons of water per year. Faucet leaks often result from deteriorating washers or gaskets.
EPA data indicated that running toilets and types of toilet leaks often waste up to 200 gallons of water per day. In many cases, running toilets result from faulty toilet flappers, which are, fortunately, inexpensive to replace.
Some of the other potential consequences of water leaks include:
- Costly repair expenses: The costs of replacing water-damaged floors and carpeting often exceed $7 per square foot.
- Health risks: Moisture and humidity worsen indoor air quality and encourage the growth of mold and mildew, which may trigger allergic reactions and respiratory concerns.
- Other utility expenses: Aside from increasing water bills, leaks may impact other energy utilities, such as those supplying water heaters.
Conserving Water in Your Bathroom
Bathrooms are areas of a home where a substantial amount of water is expended. Homeowners should assess their daily routine to recognize opportunities to conserve water, often by limiting the amount of time that water remains running. Further water savings are achieved by installing high-efficiency faucets, shower heads and toilets.
Property owners should also regularly check for any evidence of leaks. For more comprehensive whole-home water monitoring and management, homeowners might also consider the Flume Smart Home Water Monitor system.
You may also like
Water-Wise Living: Eco-Friendly Strategies for Summer Conservation at Home
5 Eco-Friendly Car Wash Cleaning Products You Should Invest In
5 Eco-Friendly Upgrades for Your Home and Outdoor Space
Easy Ways to Reduce Water Usage Inside Your Home
